In the vast landscape of language, pronouns stand as unsung heroes, quietly shaping our communication in profound ways. These humble word-warriors replace nouns, streamline our sentences, and add nuance to our expressions. But how well do we truly understand these linguistic workhorses? Let’s embark on a journey to explore the fascinating world of Types of Pronouns their Definitions with Examples, unraveling their definitions and bringing them to life with vivid examples.
What Are Pronouns? Unraveling the Mystery
At their core, pronouns are words that take the place of nouns in a sentence. They’re the chameleons of language, adapting to represent people, places, things, and ideas without constant repetition. Imagine trying to tell a story without pronouns:
“John picked up John’s book. John opened John’s book and John began to read John’s book.”
Yikes! Now, let’s see how pronouns transform this clunky sentence:
“John picked up his book. He opened it and began to read.”
Much better, right? This simple example showcases the power of pronouns in creating fluid, natural language. But pronouns do more than just replace nouns – they carry information about gender, number, person, and case, all packed into tiny packages of linguistic efficiency.
The Evolution of Pronouns: A Brief History
Pronouns aren’t just a modern convenience. They’ve been shaping human communication for millennia. In fact, linguists believe that pronouns are among the most stable elements of language, often resisting change even as other words evolve rapidly.
“Pronouns are the linguistic equivalent of cockroaches – they’ve survived countless language extinctions and will likely outlast us all.” – Dr. Emily Wordsmith, Historical Linguist
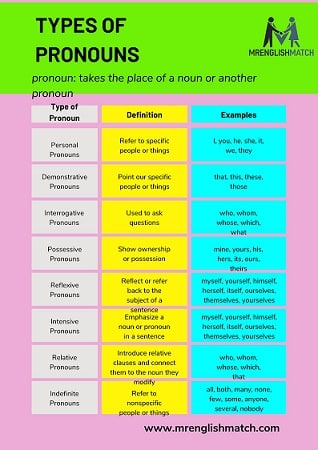
The Pronoun Panorama: 12 Types to Master
Now, let’s dive into the heart of our topic: the various Types of Pronouns their Definitions with Examples. We’ll explore 12 distinct categories, each with its own unique role in the language landscape.
Types of Pronouns: A Comprehensive Guide
Pronouns come in various forms, each serving a unique function in language. Here’s a detailed look at the types of pronouns:
Personal Pronouns
Possessive Pronouns
Reflexive Pronouns
Demonstrative Pronouns
Interrogative Pronouns
Indefinite Pronouns
Relative Pronouns
Reciprocal Pronouns
Intensive Pronouns
Distributive Pronouns
Dummy pronouns
Personal Pronouns: The “I,” “You,” and “They” of Language
Personal pronouns are the workhorses of Types of Pronouns their Definitions with Examples. They refer to specific people or things and change form based on person, number, gender, and case.
Here’s a table showcasing personal pronouns in action:
| Person | Subject | Object | Possessive | Example Sentence |
| 1st Singular | I | me | mine | I love reading books. |
| 2nd Singular | you | you | yours | Did you finish your homework? |
| 3rd Singular (M) | he | him | his | He went to the store. |
| 3rd Singular (F) | she | her | hers | She loves ice cream. |
| 3rd Singular (N) | it | it | its | It chased the ball. |
| 1st Plural | we | us | ours | We are going on vacation. |
| 2nd Plural | you | you | yours | Are you all coming to the party? |
| 3rd Plural | they | them | theirs | They won the championship. |
You might also like this:
Verbs and Their Types, Definitions, and Examples
Types of Nouns with Examples and Definitions
Types of Verbs Their Definitions with Examples
Possessive Pronouns: Claiming Ownership in Speech
Possessive pronouns show ownership or belonging. They replace possessive noun phrases to avoid repetition.
| Possessive Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| mine | That book is mine. |
| yours | Is this guitar yours? |
| his | The blue hat is his. |
| hers | The briefcase is hers. |
| its | The dog wagged its tail. |
| ours | This house is ours. |
| yours | That car is yours, isn’t it? |
| theirs | The painting is theirs. |
Possessive pronouns vs possessive adjectives: It’s important to distinguish between these two. Possessive adjectives (my, your, his, her, its, our, their) come before nouns, while possessive pronouns stand alone.
Reflexive Pronouns: When the Subject and Object Collide
What are reflexive pronouns? They’re used when the subject of a sentence is also the object, reflecting the action back onto the doer.
| Reflexive Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| myself | I saw myself in the mirror. |
| yourself | You should treat yourself to a spa day. |
| himself | He taught himself how to cook. |
| herself | She prides herself on her dancing skills. |
| itself | The cat groomed itself. |
| ourselves | We challenged ourselves to run a marathon. |
| yourselves | You all should express yourselves freely. |
| themselves | They immersed themselves in the art project. |
Demonstrative Pronouns: Pointing with Words
The Demonstrative pronouns examples show how these words point out specific people, animals, or things.
| Demonstrative Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| this | This is my new phone. |
| that | That looks like an oak tree. |
| these | These are the cookies I baked. |
| those | Those are the brightest stars in the sky. |
Interrogative Pronouns: The Question Askers
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. Here’s a list of interrogative pronouns in action:
| Interrogative Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| who | Who left this message? |
| whom | To whom should I address the email? |
| whose | Whose coat is this? |
| which | Which apple do you want? |
| what | What is the capital of France? |
Indefinite Pronouns: Embracing Ambiguity
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific people or things. Understanding the difference between indefinite and relative pronouns is crucial for mastering English grammar.
| Indefinite Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| anyone | Is anyone home? |
| everyone | Everyone is invited to the party. |
| someone | Someone called for you earlier. |
| no one | No one knows the secret. |
| everybody | Everybody loves ice cream. |
| nobody | Nobody wants to work on weekends. |
| something | I have something for you. |
| anything | Did you find anything interesting? |
| nothing | There’s nothing to worry about. |
| all | All is well with the world. |
Relative Pronouns: Connecting Clauses with Finesse
The Relative pronouns introduce relative clauses, providing additional information about a noun.
| Relative Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| who | The doctor who treated me was very kind. |
| whom | The teacher whom we met yesterday is brilliant. |
| whose | The athlete whose record was broken trained hard. |
| which | The house, which was built in 1900, needs renovation. |
| that | The book that I’m reading is fascinating. |
Reciprocal Pronouns: The “Each Other” and “One Another”
The Reciprocal pronouns express mutual actions or feelings between two or more people.
| Reciprocal Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| each other | They love each other deeply. |
| one another | The team members support one another in tough times. |

Intensive Pronouns: Adding Emphasis to Identity
Intensive pronouns emphasize a noun or another pronoun. They take the same form as reflexive pronouns but serve a different purpose.
| Intensive Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| myself | I myself will handle this project. |
| yourself | You should be proud of yourself. |
| himself | The king himself attended the ceremony. |
| herself | The queen herself made the announcement. |
| itself | The volcano itself wasn’t dangerous, but the lava was. |
| ourselves | We built this company ourselves. |
| yourselves | You can do it yourselves! |
| themselves | The actors themselves wrote the script. |
Distributive Pronouns: Dividing the Group
The Distributive pronouns refer to members of a group separately rather than collectively.
| Distributive Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| each | Each of the apples was perfectly ripe. |
| either | You can take either of the cars. |
| neither | Neither of these dresses suits me. |
| any | You can borrow any of my books. |
Dummy Pronouns: The Placeholders of Language
The Dummy pronouns, also known as expletive pronouns, don’t refer to any specific person or thing but are necessary for grammatical structure.
| Dummy Pronoun | Example Sentence |
| it | It is raining heavily. |
| there | There are many houses on this street. |
Pronouns in Action: Real-World Examples and Usage
Now that we’ve explored the various types of pronouns, let’s see how they shape our everyday communication.
Literature: How Great Authors Wield Pronouns
Great writers use pronouns to create rhythm, emphasize themes, and develop characters. Consider this excerpt from Virginia Woolf’s “Mrs. Dalloway”:
“She had a perpetual sense, as she watched the taxi cabs, of being out, out, far out to sea and alone; she always had the feeling that it was very, very dangerous to live even one day.”
The repeated use of “she” creates a sense of isolation and introspection, perfectly capturing the character’s state of mind.
Everyday Speech: Pronoun Patterns We Often Overlook
In casual conversation, we often use pronouns in ways that might surprise us:
- Singular “they”: “Someone left their umbrella in the office. Could you please let them know where they can find it?”
- Generic “you”: “You never know what life will throw at you.”
- Inclusive “we”: “We need to take better care of our planet.”
Professional Writing: Pronoun Precision in Business and Academia
In formal writing, Types of Pronouns their Definitions with Examples usage requires extra care:
- Clarity is key: “The marketing team presented its findings to the board.” (Not “their” if referring to the team as a single entity)
- Avoiding gender bias: “Each employee should submit their report by Friday.” (Instead of “his or her”)
- Maintaining objectivity: “This study demonstrates that…” (Instead of “We believe that…”)
The Pronoun Puzzle: Common Challenges and Solutions
Even native speakers sometimes struggle with pronoun usage. Here are some common pitfalls and how to avoid them:
- Agreement issues: Ensure pronouns match their antecedents in number and gender.
- Incorrect: “Each student must bring their book.”
- Correct: “Each student must bring his or her book.” (Or use plural: “All students must bring their books.”)
- Clarity conundrums: Avoid ambiguous pronoun references.
- Ambiguous: “John told Tom that he was wrong.”
- Clear: “John told Tom, ‘You are wrong.'”
- Who vs. Whom: “Who” is a subject pronoun, while “whom” is an object pronoun.
- Subject: “Who wrote this letter?”
- Object: “To whom should I address this letter?”
- Gender-neutral language: In many contexts, it’s best to use inclusive language.
- Instead of: “A doctor should always wash his hands.”
- Use: “Doctors should always wash their hands.”
Pronouns Across Languages: A Global Perspective
In English language, the Types of Pronouns their Definitions with Examples might seem complex, but they’re relatively simple compared to some other languages:
- Japanese has multiple first-person pronouns that vary based on the speaker’s gender and the formality of the situation.
- Some Native American languages have inclusive and exclusive “we” pronouns, distinguishing between “we including you” and “we excluding you.”
- Many languages, like Spanish and French, have gendered pronouns for inanimate objects.
The Future of Pronouns: Trends and Predictions
Language is ever-evolving, and pronouns are no exception:
- Gender-neutral pronouns are gaining traction, with “they” increasingly accepted as a singular pronoun.
- Neopronouns like “xe/xem” or “ey/em” are emerging in some communities.
- AI and pronouns: As AI language models advance, they’re becoming more adept at nuanced pronoun usage, potentially influencing human communication.
Mastering Pronouns: Tips and Tricks
To improve your pronoun game:
- Read extensively: Exposure to well-written text improves intuitive understanding.
- Practice with exercises: Try online quizzes or workbooks focused on pronoun usage.
- Use mnemonic devices: For example, “If ‘he/him’ fits, it’s ‘who’; if ‘him’ fits alone, it’s ‘whom’.”
Conclusion: The Subtle Strength of Pronouns
Pronouns may be small, but they’re mighty. They streamline our speech, add nuance to our writing, and reflect our ever-changing cultural landscape. By mastering the art of pronoun usage, we not only communicate more effectively but also gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate beauty of language.
So the next time you casually toss a “they” or “it” into conversation, take a moment to marvel at the linguistic journey that brought that tiny word to your lips. After all, in the grand narrative of language, pronouns are the unsung protagonists, quietly shaping our stories one sentence at a time.

John Robert is a seasoned grammar enthusiast and the insightful voice behind MrEnglishMatch. With years of experience in language arts and a passion for clear, effective communication, John’s blog posts blend expertise with approachable advice. His deep understanding of grammar and style helps readers sharpen their writing skills and master the nuances of English. When not blogging, John enjoys exploring new languages and reading classic literature.







