Idioms are an essential part of the English language, adding color, nuance, and cultural depth to communication. Whether you’re trying to “break the ice” in a conversation or “bite the bullet” in a tough situation, idioms play a significant role in making language vibrant and relatable. These English idioms help you deep into what idioms are, their types, meanings, origins, and how to effectively use them in daily life.
What Are Idioms?

Idioms are phrases or expressions with meanings that are not immediately apparent from the literal words used. Instead, their meanings are often metaphorical, culturally specific, and context-driven. For example:
- Break a leg: Despite its literal meaning, this phrase is commonly used to wish someone good luck, especially before a performance.
Idioms reflect the culture and history of a language, making them integral to understanding and using English effectively. Learning idioms not only enhances communication skills but also provides insight into how native speakers think and express themselves.
Types of Idioms and Examples
Idioms come in various forms, each serving a unique purpose in language. Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
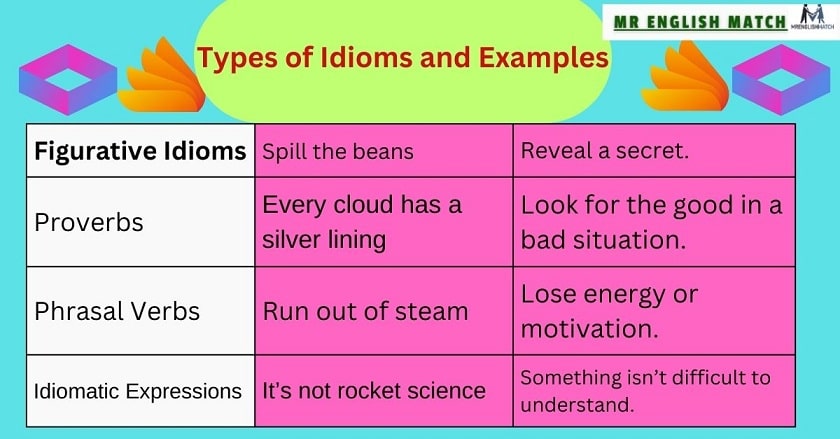
Figurative Idioms
These idioms use metaphorical meanings to convey messages.
- Spill the beans: Reveal a secret.
- Under the weather: Feeling sick.
Proverbs
Proverbs are short, commonly known sayings that express wisdom or truth.
- Actions speak louder than words: What you do is more important than what you say.
- Every cloud has a silver lining: Look for the good in a bad situation.
Phrasal Verbs
These are idiomatic expressions formed by combining a verb with a preposition or adverb.
- Run out of steam: Lose energy or motivation.
- Bring up: Mention or raise a topic.
Idiomatic Expressions
These include sayings unique to specific regions or cultures.
- It’s not rocket science: Something isn’t difficult to understand.
- Barking up the wrong tree: Making a mistake or misjudgment.
Break a Leg: Why It’s More Than Just a Phrase
Appositive Phrase: A Comprehensive Guide
Common Idioms and Their Meanings
Idioms are often used in daily communication, and understanding their meanings can improve fluency. Below is a table of common idioms with their meanings:
| Idiom | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Break a leg | Good luck |
| Hit the nail on the head | Get something exactly right |
| Piece of cake | Something very easy |
| Bite the bullet | Face a difficult situation with courage |
| Go big or go home | Take bold action |
These common American idioms are frequently heard in movies, TV shows, and conversations, making them essential for English learners.
Funny and Creative Idioms
Humor and creativity shine through many idioms, often making them memorable. For example:
- When pigs fly: Something that will never happen.
- Hold your horses: Be patient.
Funny idioms like these often have fascinating origins, making them enjoyable to learn and use.
Idioms for Specific Situations
Turning Something Bad into Something Good
Some idioms focus on optimism and resilience:
- Every cloud has a silver lining: Finding the good in bad situations.
- Make lemonade out of lemons: Turn challenges into opportunities.
Idioms for Describing Powerful People
When describing influential individuals, these idioms are apt:
- Hold all the cards: Be in a position of control.
- Top dog: The person in charge or the best at something.
Idiom Examples for Kids
Teaching idioms to kids can be a fun and educational activity. Here are some simple idiom examples for kids:
- Cold feet: Feeling nervous before an event.
- Butterflies in your stomach: Feeling anxious or excited.
Using stories or cartoons featuring idioms can help children understand their meanings while keeping the learning process enjoyable.
Origins of Idioms and Common Sayings
Many idioms have fascinating backstories tied to historical events, cultural practices, or even folklore. For instance:
- Break the ice: Originates from ships breaking through ice to pave the way for others.
- Barking up the wrong tree: Stems from hunting, where dogs would bark at the wrong tree while chasing prey.
Understanding the origin of common phrases can provide deeper appreciation and insight into the English language.
Why Learn Idioms?
Learning idioms enhances language skills, allowing speakers to:
- Communicate more effectively: Idioms convey emotions and ideas concisely.
- Understand cultural nuances: Many idioms are rooted in cultural practices and history.
- Engage in richer conversations: Idioms make interactions more colorful and engaging.
Idioms are also a vital part of daily phrases. By incorporating them, learners can master english and idioms together, making their speech and writing more natural.
Tips for Learning and Using Idioms
- Practice in Context: Use idioms in sentences to understand their meanings better.
- Watch Movies or Shows: Many American TV shows and movies use idioms frequently.
- Explore Resources: Use tools like Merriam-Webster Idioms and Phrases for accurate definitions.
- Create Flashcards: Write idioms and their meanings to practice daily.
Conclusion
Idioms are the heart and soul of the English language, adding charm, wit, and depth to communication. Whether you’re exploring idioms usa, teaching idiom examples for kids, or mastering common sayings, idioms bring English to life in ways that resonate deeply with both native speakers and learners.
Start using idioms today to enrich your conversations, expand your vocabulary, and connect with others on a cultural level. After all, there’s nothing quite like speaking the language with idiomatic flair!








